An IUI or intrauterine insemination consists of placing sperm previously prepared in the laboratory directly into the uterus. The procedure is performed by a gynaecologist and is painless. In France, intrauterine insemination is the first-line treatment. It is therefore the most commonly operated technique in fertility assisted, accounting for 43% of attempts in 2017. Here are the different stages of the treatment:
As part of an IUI protocol, ovarian stimulation is used to improve ovulation and control its timing. The hormonal treatment induces the maturation of up to three ovarian follicles. Find out more about the ovarian stimulation procedure in our dedicated article.
The aim of intrauterine insemination is to facilitate the meeting between the oocyte and the spermatozoon. Ovulation is triggered, allowing the oocyte to mature and be released by the ovary into the Fallopian tubes (where fertilisation will take place).
On the day of insemination, sperm is collected by masturbation after 2 to 5 days of sexual abstinence. The sperm is prepared in the laboratory and the most mobile spermatozoa are selected for insemination. A minimum of one million sperm is required for insemination.
94% of IUIs are artificial inseminations with the spouse's sperm (IAC) and 6% with donor sperm (IAD).
CAI is recommended in cases of moderate sperm abnormalities (with at least one million motile spermatozoa). It will also be prescribed for couples with idiopathic infertility and in cases of ovarian insufficiency, mild endometriosis, or cervical abnormality.
Artificial insemination using donor sperm is used in cases of male infertility (azoospermia: total absence of sperm in the partner's sperm or severe teratospermia: numerous sperm abnormalities). Sperm donation may also be considered when the spouse presents a high risk of transmitting a genetic disease to his or her offspring.
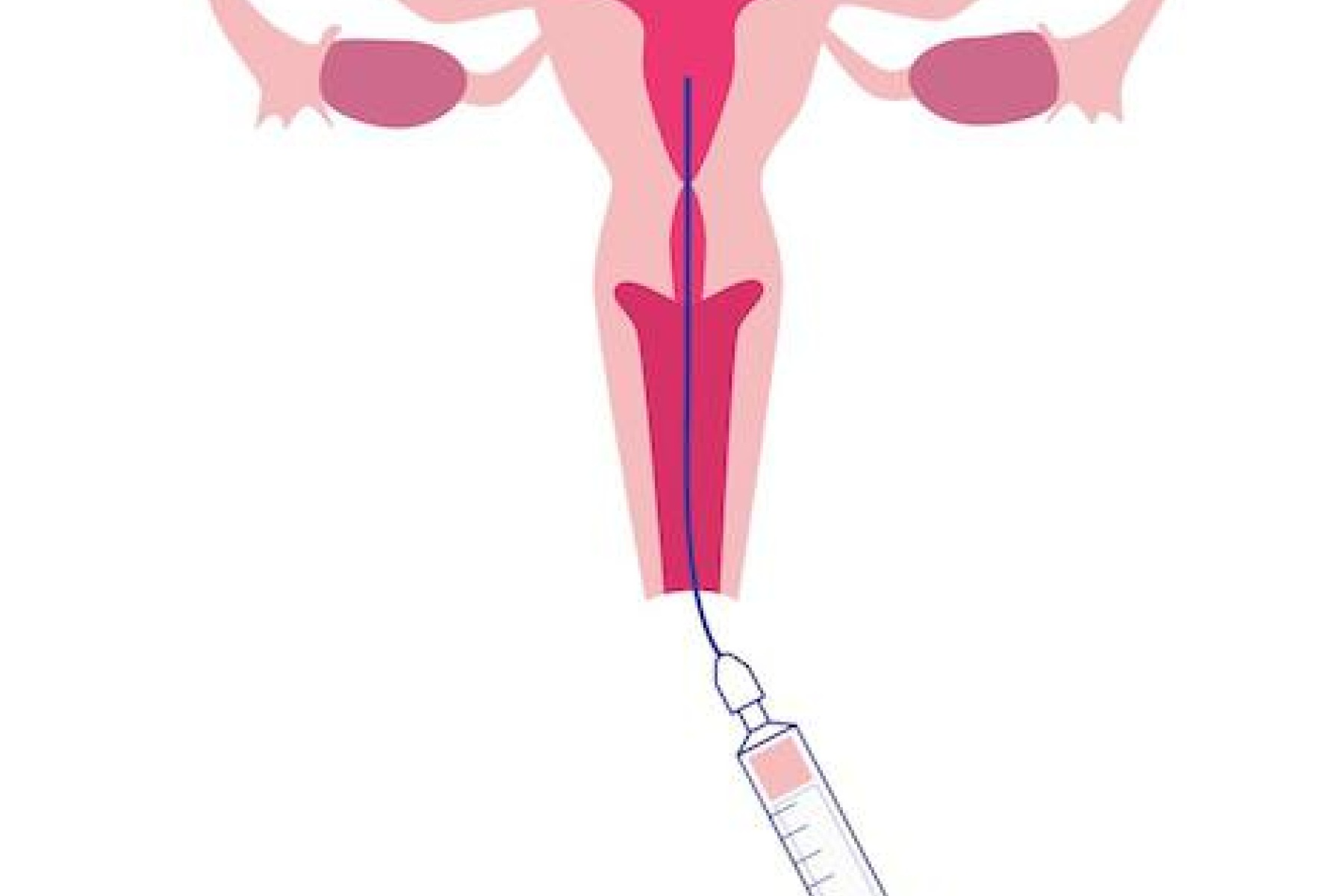
It takes place at the fertility centre, 36 hours after ovulation is triggered. It takes place in the gynaecological position: the selected spermatozoa are placed in a flexible tube (a catheter). The catheter is used to deposit the sperm in the uterine cavity.
Intrauterine insemination is the most commonly operated technique in France, but it is far from the most effective! Only 5,868 babies were born following the 49,367 inseminations carried out in 2017. This type of fertility method has a success rate of around 12%. It is important to note that inseminations carried out with donor sperm (a man with no sperm abnormalities) have a birth rate of 21%.